CNC Machine 1
3 Basic Motion Types in a CNC Machine
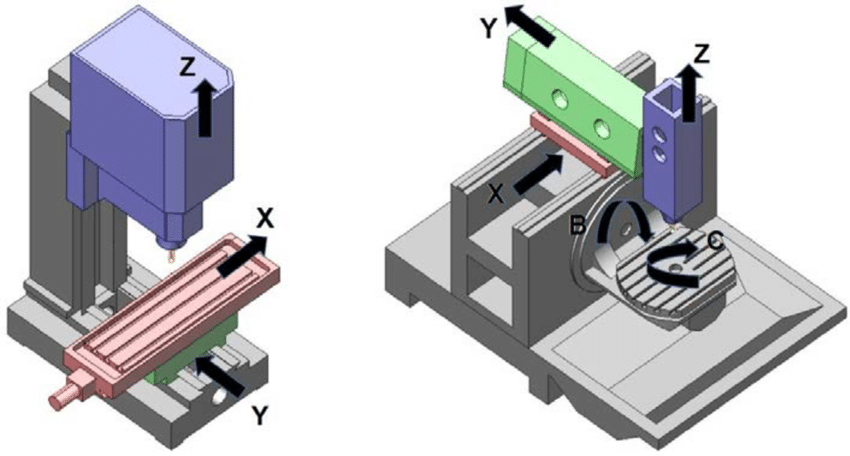 CNC Machine A Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC) machine may have more than one motion type that it uses,
CNC Machine A Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC) machine may have more than one motion type that it uses,
but there are three most common motion types that are easy to remember.
These are the Rapid Motion, the Straight Line Motion, and the Circular Motion.
All of these motion types may seem different but they share two things in common,
which would be that they are all modal and the endpoint of each motion is specified in motion command.
By being modal it means that the motion type would be in effect until changed otherwise.
CNC Machine
3 common motion types:
1.)Rapid Motion Type
Rapid motion type is also called Positioning.
The way this motion type is used is through utilizing the fastest rate possible of the command motion of the machine.
Example uses of rapid motion are moving to clear obstructions,
placing cutting tools to and from the desired position,
and any program that provides non-cutting in their schemes.
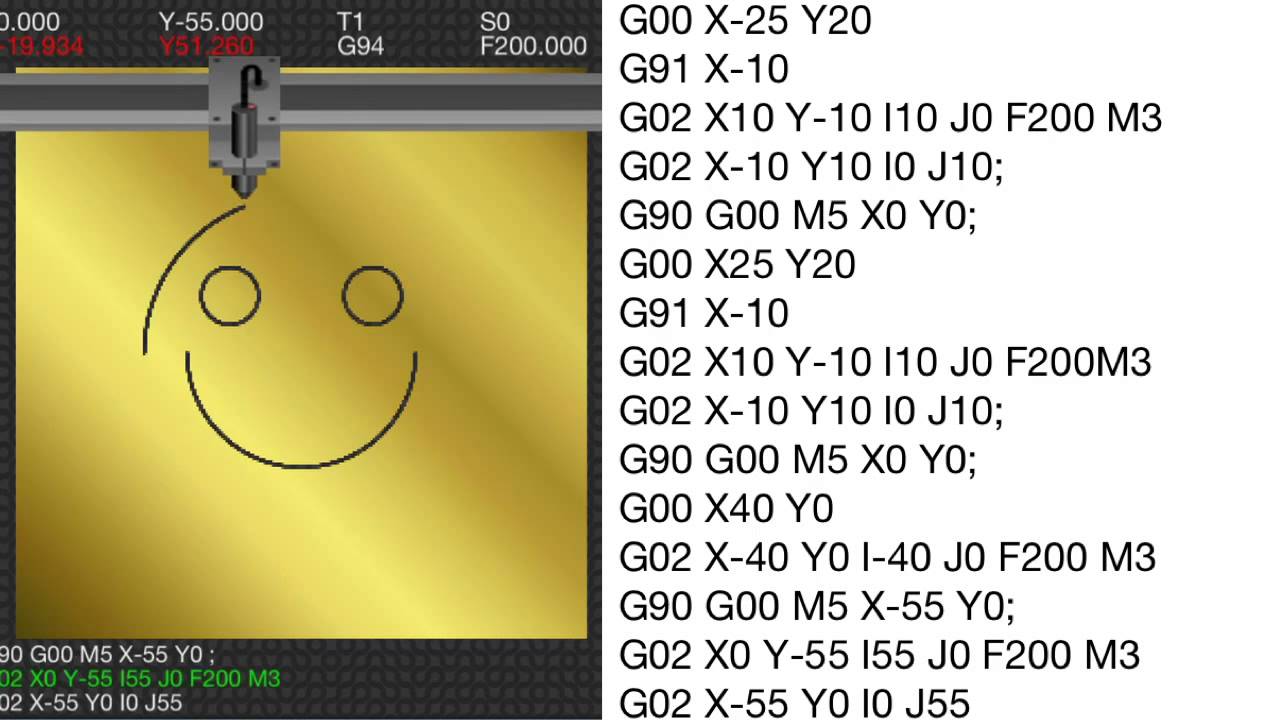
The command that is usually programmed to a CNC machine is G00 because in this command,
the end point for the rapid motion would be specified.
The CNC machine,
with most controls given, will be able to move as fast as possible in all commanded axes.
In the case of rapid motion, one axis may be able to reach its end point before other axes.
Straight line movement will not occur with type of rapid command function and the programmer of the machine
must take into account that there are no obstructions to avoid. Straight line motion
will happen even during rapid motion commands when done with other controls.
2.)Straight Line Motion
This type of motion would allow the programmer of the machine to command perfectly straight line movements within the machine.
Unlike the rapid motion type,
the straight line motion would allow the programmer to vary the rate of the motion or feed rate to be used during the movement.
Examples of using straight line motion would be turning a straight diameter,
taper, when milling straight surfaces,
and when drilling for this is because these examples require straight cutting movement.
The common word to specify a straight line motion into a machine would be G01,
for within this command the programmer will include the preferred end point within each of the axes.
3.)Circular Motion
This motion type would cause the machine to move in the direction of a circular path and is used to generate the radii in machining.
When talking about points on circular motion feed rate,
it is equal to that of straight line motion.
Other than that of straight line motion and rapid motion,
there are two G codes that are commonly used when programming a circular motion into a machine.
These are G02 and G03.
G02 is used when the programmer desires a clockwise motion into the machine
while G03 is used to make an anti-clockwise motion.
To know which of the commands to use,
the programmer must view the movement with the same perspective as to what the motion of the machine will be,
may it be clockwise or anti-clockwise.
Another requirement that would be programmed into a machine that would be using circular motion is that
the programmer must specify the radius of the arc that is to be generated.
With brand new technological advances in CNC, an “R” word is now used to specify the radius.
For older controls in CNC machinery, an “I”, “J”, and “K” are used to specify location of the center point of the arc.
 CAM: A Vital Component of CNC
CAM: A Vital Component of CNC
Computer Aided Manufacturing started being used by automotive and aerospace component manufacturing companies.
This sped up the manufacturing process and thus increased efficiency ratings.
However, the introduction of CAD into the industrial sector did not eliminate the need for skilled professionals.
In fact, the operation of this program requires a higher degree of skill in terms of being computer literate.
Flaws
The CAM system is a flawless solution.
However speedy the system becomes, it still has faults that may hamper production.
Since CAM generates a code for the least capable machine,
an improperly set CAM software required heavy manual editing. In this case,
editing such a code is a tedious and drawn-out process that takes a lot of time and effort
(something that big-time companies cannot spare).
Another problem that you have to face is the data exchange that has to take place when integrating
CAM with other components (CAD/CAM/CAE PLM).
It becomes necessary for the CAM operator to export the data in a more compatible data format.
And since the output stack of CAM is a
G-code text file—sometimes containing thousands of commands—the operator is then faced with a very serious time problem.
CAM cannot reason. In this case, it cannot figure out the right toolpath for mass production.
Operators would still have to select the type of tool to be used,
the machining process that should be followed, and the path to be used.
This means that the CAM cannot adjust to wear issues and sudden changes.
It needs to be reprogrammed to be able to work efficiently. Furthermore,
mass production increases the likelihood of errors to occur in the production cycle.
PROS
CAM can cut cycle time significantly.
This means that with the proper people and the proper tools, a more efficient production method can be obtained.
A lower cycle time means that you can produce more components in a lesser time.
And since the main users of CAM and CNC are big manufacturers with deadlines, it is of the utmost priority to cut cycle time.
Another advantage that could be gained by CAM software is the increase in machine life.
Since the process is automated,
the system can keep track of certain variables that allow it to adjust to the conditions of the machine that is operating under it.
This means that the life of the machine can be extended by adjusting
the performance of the machine in order to avoid overworking it.
Quality can also be taken into account in this scenario.
It is because the system also monitors slight differences in the production environment.
Furthermore, the intricate designs that cannot be achieved by human engineers can be achieved by the machines.
Also, these designs can be completed at a faster rate compared to manual operations.
Another factor that should be considered would be the error ratio of the production of any components.
Conclusion
So, CAM is a very important aspect of production. However,
the need for skilled operators still exists as programming and setting up these machines decide the
fate of the manufacturing process. However, the increased automation and
efficiency provided by such a system makes programming and setting up of these systems the only jobs of the operators.
This also allows operators to be more productive as they do not have to watch any
single machine for more than the required amount of time.
Computer Numerical Control Machines are sophisticated instruments that only trained CNC operators should operate them.
There are certain rules and guidelines to consider if you are planning to use a CNC machine by yourself.
CNC checklist before startup
Before starting up the Computer Numerical Control Machine, there are safety rules that must be considered first.
First important aspect before starting up the CNC machine is to ensure your own safety,
therefore wearing protective gear, such as eye glasses and short sleeved shirts is an important dress code during CNC operation.
You should also be careful whenever you are handling tools and sharp edged work pieces to avoid any accidents.
You must also ensure that the cutting tools are fastened in the machine spindle to avoid any movement during the cutting operation.
 Actual Startup, Operation and Machine Setup of the CNC
Actual Startup, Operation and Machine Setup of the CNC
The Computer Numerical Machine startup procedure varies depending
with the type of machine being used but usually there is a main power switch
or a circuit breaker to turn it on. Some machines also require hydraulics or air pressure before it starts up.
When the Computer Numerical Machine starts up, the machine usually starts at its Machine Home Position.
The Machine Home Position allows the control and the machine to have a preset starting position for all its axes.
After startup, the CNC machine must be sent to this position before the work begins.
This position will later be changed to an appropriate location whenever you are machining a particular part of a product.
The Tool Length Offset Value or TLO is the distance from the tip of the tool from the spindle in the Home Position.
The TLO must be set for each tool in the current job.
The TLO can be set using a height gage, fixture location,
as well as the reference tool. When these values are determined, they are stored in the
 Controller to be used during the program operation.
Controller to be used during the program operation.
After setting the Tool Length Offset Value it is time to setup a part origin of a CNC machine.
Setting up the part origin on a CNC machine is the same as setting up a conventional machine.
It usually involves positioning the axes to a point where the plan designates as its origin.
There are many ways to locate the position on the reference point, it is by using edge finders, wigglers or magnifying glasses.
After setting up the whole system for the Computer Numerical Control, it is time to Load the program to the machine.
Program loading is different for each machine.
Some machines have tape readers to input the program into the Computer Numerical Control Machine’s memory.
Newer machines have internal or external floppy devices to input the program to the machine.
After the program is loaded to the machine, the CNC machine is now ready to use.
There are certain instances when you have to change the tools in the Computer
Numerical Control manually during machine operations. When a certain machining operation is complete,
the program will move the aces to the tool change position and display the next tool needed.
It is now the job of the Machine operator to remove and replace it with the next tool.
Extra Care must be taken whenever you are starting operations with the CNC machine,
any mistake taken during the part of the operation may lead to serious injuries from the machine operator.
CNC Programming Tips the Professional Way
When a program is completed and sent to the Computer Numerical Control Machine, the programming process is over.
All calculations were made and the algorithm fully written.
But the question is the programmer’s job really finished?
When is the programmer’s responsibility really over?
And how can we evaluate the type of program that the Computer Numerical Control Machine programmer did?
The fairest and reasonable answer to those questions would basically
when a part has been machined under the most optimized working conditions.
Therefore the Programmer’s responsibility does not end after he or she finishes the program.
We could say that the program at this stage is still very much in the development process,
because most of the programming considerations were based on certain assumptions and there are a
lot of external factors that may affect the outcome of the product.
Every Computer Numerical Control programmer should have an effort to be in the touch with the actual production.
In the field of software development, Constant communication with your colleagues as well as actual machine operators of the CNC
will help you to improve your own program. Because most of the time the CNC machine operators
are a good source of constructive ideas, improvements and suggestions.
A good CNC programmer should talk, ask questions to them and most importantly listen to what they have to say.
Programmers who never put their foot in the actual machining process and think they are always right are all on the wrong track.
Exchanging ideas with CNC machine operators,
asking questions and seeking answers is the only way to be fully aware of what is going on in the machine.
Whenever you start a Computer Numerical Control Program the first time it is important to check its Program Integrity.
A new and unproved program is a potential source of problems.
During Manual Programming in CNC,
 mistakes are more common than when the program is made in a CAM program.
mistakes are more common than when the program is made in a CAM program.
A good way to look at a new program is through the machine operator’s perspective.
Experienced Machine Operators take a direct approach when running a program for the first time.
That means that they wont take any chances of mistakes with the actual running of a
program therefore a good programmer must take note of any comments that the Machine operator will say about the program.
What does an experienced Machine Operator look for in a new part of a program?
Most of the Machine operators would say that the first and most important
thing to be checked on a Computer Numerical Control Program is its consistency.
Therefore a machine operator looks at how a CNC programmer does its own programming
, is the way you create your own algorithms the same as the other ones.
Machine Operators take note with this kind of Information.
 Upgrading your CNC Program
Upgrading your CNC Program
Whenever you upgrade your own program, it means that you are strengthening or enriching it,
therefore making it better than it was before.
Upgrading would be based on this standard,
It is to decrease the production cost without compromising the quality of the part being
manufactured or the safety of the Computer Numerical Control Machine Operator.
One of the Most Common forms of Program Optimization is doing some minor changes to the spindle
as well as the feed rates of the machines. This process is called cycle time optimization,
slightly increasing the spindle speed and feed rates of these machines will decrease the time it takes to finish the part.
And when we compare it to mass production, saving one second for each
part in a batch of 3600 pieces would mean an hour saved.
Efficiency in the rate of production is a very important aspect in Mass Production.
 لمعرفة اخر المنتجات الخاصة بنا وعروضنا المميزة يرجى الاشتراك بصفحاتنا على مواقع التواصل الاجتماعي:
لمعرفة اخر المنتجات الخاصة بنا وعروضنا المميزة يرجى الاشتراك بصفحاتنا على مواقع التواصل الاجتماعي:
صفحتنا على الفيسبوك=> Gahzlystore
صفحتنا على تويتر=> Gahzlystore

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.